- Study of PA influence on consumption of food, obesity and course of experimental diabetes type-2 under the influence of gold thioglucose;
- Assessment of PA activity in the model of experimental diabetes type-2 induced by single streptozotocin administration;
- Assessment of PA activity in the model of experimental diabetes type-1 induced by alloxan administration;
- Study of the effect on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism and body weight in metabolic syndrome complicated by hyperphagia and induced by a high-caloric diet – ” fast food diet” ;
- Assessment of PA efficiency in the model of an experimental prolonged streptozotocin diabetes complicated by “diabetic foot” pathology;

- Study of hypolipidemic actions;
- Study of anti-atherosclerotic effect in rabbits;
- Study of anti-atherosclerotic effect in guinea pigs;
- Study of antioxidant properties on the model of maximum physical activity;
- Study of mechanisms of anti-atherogenous action;
- Assessment of anti-proliferative action of PA in epithelial cells;
- Analysis of PA influence on enzymatic activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glyutaril coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA-reductase);
- Assessment of anti-inflammatory action of PA in the model of carrageenan bulla (in vivo);
- Assessment of PA activity in the model of metabolic syndrome in rats;
- Study of mechanisms of anti-atherogenic and hypoglycemic action.
Biochemical tests:
|
– Glucose, – Glucose-tolerance test, – Lactate, – Glycosylated hemoglobin, – Insulin, – Glucagon, – Adiponectin, – Leptin, -Triglycerides, |
– Total cholesterol, – α–cholesterol, – Prothrombin time, – Activated partial thromboplastin time, – Fibrinogen, – Malondialdehyde/ – Reduced glutathione, – Nitric oxide. |
Hematologic tests:
– hemacyte,
– hematocrit,
– reticulocytes.
Physiological researches:
– neurologic status,
– pain and tactile sensitivity,
– physical activity,
– emotional status,
– cognitive functions,
– endurance test “Forced swimming”,
– endurance test “Running wheel”.
Microscopic morphological examination:
– histology
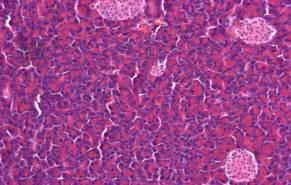
Normal structure of pancreas of an intact rat.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining, ?200
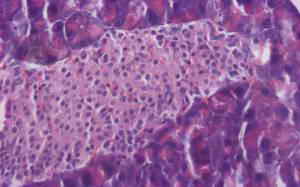
Pancreas of a rat with streptozotocin-induced diabetes: pronounced lipomatosis, hyperplasia of insular islands. Hematoxylin and eosin staining, ?200
– immunohistochemistry
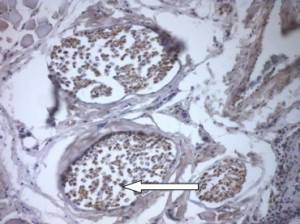
Normal structure of foot skin of an intact rat: nervous fibers without aberration. Immunohistochemical staining against neyronal marker PGP 9.5 in axial cylinder. ?200
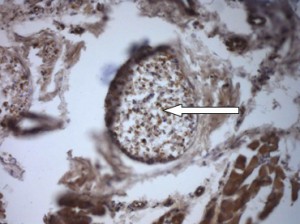
Foot skin of a rat with “diabetic foot” pathology: nervous fibers have foci of demyelination and evidences of degeneration of tiroidea substance axial cylinders. Immunohistochemical staining against neyronal marker PGP 9.5 in axial cylinder. ?200
-
- Kovaleva M.A., Kokareva M.N., Makarova M.N., Makarov V.G. Antidiabetic effect of ubidecarenone in rats // Phytopharm 2012. Obzory po klinicheskoj farmacologii i lekarstvennoj terapii. 2012. 10(2). M70.
- Kovaleva M.A., Makarova M.N., Shikov A.N., Makarov V.G., Djachuk G.I., Khodko S.V. Antidiabetic effect of larix sibirica exstract in rats // Phytopharm 2011. 15th International congress. Book of Nuremberg, Germany, 2011. 63.
- Makarova M.N., Tesakova S.V., Makarov V.G., Samusenko I.A. Experimental modeling of diabetes mellitus and its complications // Phytopharm. 2008. 12 th International congress. Book of Leiden. Netherlands. 1-4 July 2008. P.71.
- Obukhova V.V., Makarova M.N., Khodko S.V., Abrashova T.V., Sokolova A.P. An investigation of the herbal mixtures influence on the blood coagulation system in a rabbit experimental atherosclerosis model // Phytopharm 2011. 15th International congress. Book of Nuremberg, Germany, 2011. 79-80.
- Obukhova V.V., Ivanova S.A., Makarova M.N., Khodko S.V. An investigation of the herbal mixtures influence on the bile composition in a rabbit experimental atherosclerosis model // Phytopharm 2011. 15th congress. Nuremberg, Germany, 2011. 80-81.
- Obukhova V.V., Makarova M.N., Khodko S.V., Abrashova T.V., Sokolova A.P. An investigation of the hypolipidemic activity of herbal mixtures in wistar rats // Phytopharm 2011. 15th congress. Nuremberg, Germany, 2011. 78-79.
- Obukhova V.V., Makarova M.N., Khodko S.V., Stephanov S.Y. An investigation of the anti- atherosclerotic activity of herbal mixtures in chinchilla rabbits // Phytopharm 2011. 15th congress. Nuremberg, Germany, 2011. 82-83.
- Obukhova V.V., Selezneva A.I., Makarova M.N., Khodko S.V. An investigation of the anti-oxidant activity of herbal mixtures on an experimental hyperlipidemia model in wistar rats // Phytopharm 2011. 15th congress. Nuremberg, Germany, 2011. 81-82.
- Raasmaja Atso, Kovaleva M.A., Makarova M.N., Li Xiang Ming, Zou Jianqiang, Zhu Guo-Guang, Pozharitskaya O.N., Makarov V.G., Shikov A.N., Hiltunen Raimo Metabolic effects of Citrus Grandis whole fruits extract in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats // Phytopharm 2012. Obzory po klinicheskoj farmacologii i lekarstvennoj terapii. 2012. 10( 2).
- Shikov A.N., Pozharitskaya O.N., Makarova M.N., Kovaleva M.A., Laakso I., Dorman H.J.D., Hiltunen R., Makarov V.G., Galambosi B. Effect of Bergenia crassifolia L. extracts on weight gain and feeding behavior of rats with high-caloric diet-induced obesity // Phytomedicine. 2012. 19. 1250-1255.
- Дьячук Г.И., Шиков А.Н., Лапкина Г.Я., Макаров В.Г., Макарова М.Н. Методические рекомендации по доклиническому изучению безопасности и эффективности фитопрепаратов. Методическое пособие // Под ред. проф. д.м.н.Дьячука Г.И., проф. д.м.н. Макарова В.Г. – СПб: Из-во СПбГМА, 2010, 88с.
- Ковалева М.А., Макарова М.Н., Иванова С.А. Изучение сахароснижающего и антиоксидантного действия комплекса полигидроксинафтохиноновых пигментов из панциря морских ежей на модели экспериментального стрептозотоцин-индуцированного диабета // Современные проблемы медицинских и фармацевтических наук: Сборник материалов международной научно-практической конференции. – Днепропетровск: Организация научных медицинских достижений «Salutem», 2012. –С. 42-44.
- Kovaleva M.A., Selezneva A.I., Makarova M.N., Makarov V.G., Zabozlaev A.A., Dyachuk G.I. Experimental efficiency ubidecarenone by metabolic syndrome and arterial hypersthenes // PREVENTIVE AND CLINICAL MEDICINE. – 2012. – Vol. 45(4). – P. 81-84. SUMMARY. Specific substans ubidecarenone with increased bioavailability was studied. Concentration of glucose, insulin, cholesterol, low density lipoprotein and high-density lipoprotein in the blood plasma. Blood pressure is determined not invasive. Ubidecarenone effectively normalized metabolism and decreased blood pressure. Ubidecarenone can be used as a tool in antioxidant therapy initial stages of the diseases associated with oxidative stress, such as in the treatment metabolic syndrome and hypertension [Full text is available in Russian].
- Макаров В.Г., Макарова М.Н., Проскурина И.А., Богданов А.Н., Сомов Д.В. Методические рекомендации по доклиническому изучению лекарственных средств для коррекции сахарного диабета, ожирения и метаболического синдрома // В кн.: Руководство по проведению доклинических исследований лекарственных средств. Часть первая. –М. Гриф и К, -2012. -944 с.
- Рыженков В.Е., Макаров В.Г., Ремезова О.В., Макарова М.Н. Методические рекомендации по изучению гиполипидемического и антиатеросклеротического действия лекарственных средств // В кн.: Руководство по проведению доклинических исследований лекарственных средств. Часть первая. –М. Гриф и К, -2012. -944 с.
- Selezneva A.I., Kovaleva M.A., Makarova M.N., Dyachuk G.I., Makarov V.G. Simulation of metabolic syndrome in rats with spontaneous hypertension // Proceedings of the 2nd annual scientific-practical conference “The Science of Laboratory Animals: Modern Approaches”, St. Petersburg, December 21-22, 2012 – P. 15-16.
- Физиологические, биохимические и биометрические показатели нормы экспериментальных животных. Справочник / Под ред.: д.м.н. Макарова В.Г., д.м.н. Макаровой М.Н.- СПб: Из-во «ЛЕМА», 2013. -116 с.
- Kashkin V.A., Selezneva A.I., Kovaleva M.A., Makarenko I.E., Makarova M.N., Makarov V.G. Therapeutic activity of new drag from hydrobionts in the model of metabolic syndrome in rats // The 17th international congress. Phytophrm, 2013. Vienna, Austria, 8-10 July 2013. Obzory po klinicheskoj farmacologii i lekarstvennoj terapii. – Vol. 11. – P. 46.
- Makarenko I.E., Selezneva A.I., Pozharitskaya O.N., Shikov A.N., Makarova M.N., Makarov V.G. Effects of lipid extract of sea urchins gonads in metabolic syndrome animal model // Book of Abstracts. 61st International congress and annual meeting of the GA. 1st -5th September 2013, Munster, Germany. –PB44.
- Kovaleva M.A., Ivanova S.A., Makarova M.N., Pozharitskaya O.N., Shikov A.N., Makarov V.G. Effect of a complex preparation of sea urchin shells on blood glucose level and oxidative stress parameters in type ii diabetes model // Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology. – 2013. – Vol. 76(8). – P. 27-30. https://doi.org/10.30906/0869-2092-2013-76-8-27-30 SUMMARY. The experimental preclinical study on mice showed that a complex of polyhydroxylated naphthoquinone pigments and minerals from shells of sea urchins decreases the concentration of glucose, stimulates the synthesis of phospholipids in liver, and has antioxidant properties. On the model of streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced type II diabetes, this complex of polyhydroxylated naphthoquinone pigments and minerals from sea urchin shells exhibited activity after administration for 10 days in a dose of 1.8 mg/kg [Full text is available in Russian].
- Kovaleva M., Kryshen K., Makarova M., Makarov V. Age of formation of streptozotocininduced diabetes in rats // International Bulletin of Veterinary. – 2014, №4. – P. 90-96. SUMMARY. In experimental preclinical studies conducted in rats lines Wistar, found that the concentration of glucose in the blood can not be the sole criterion for the development of experimental pathology (streptozotocininduced diabetes). The optimum age of laboratory rats for inclusion in studies and formation of experimental pathology for more than 7 weeks. In experimental preclinical studies conducted in rats line Wistar, found that the concentration of glucose in the blood can not be the sole criterion of experimental pathology (streptozotocin-induced diabetes). The aim of the present study was to investigate the optimal experimental conditions, namely, the age category of animals for experimental modeling streptozotocininduced diabetes. Experiments were performed in Wistar rats at the age of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 12 weeks. It has been shown that the response to administration in streptozotocin dose of 65 mg / kg laboratory animals older had a high and stable concentration of glucose in the blood. The results indicate that the optimal age of laboratory rats to study entry and formation of experimental pathology over 7 weeks [Full text is available in Russian].
- Макаренко И.Е., Фаустова Н.М., Ванатиев Г.В., Уракова И.Н., Пожарицкая О.Н., Макарова М.Н., Макаров В.Г., Шиков А.Н. Оценка эффективности препарата из гонад морских ежей // Фармация.– 2015, № 2. –С. 47-50.
- Pozharitskaya O.N., Shikov A.N., Laarso I., Seppanen-Laarso T., Makarenko I.E., Faustova N.M., Маkarova M.N., Makarov V.G. Bioactivity and chemical characterization of gonads of green sea urchin Strongylocentrotus drobachiensis from Barents Sea // Journal of Functional Food. – 2015, № 17. – P. 227-234.
- Пожарицкая О.Н., Шиков А.Н., Макарова М.Н., Селезнева А.И., Макаренко И.Е., Макаров В.Г. Эффективность стандартизированного экстракта из гонад зеленых морских ежей на экспериментальной модели метаболического синдрома // Экспериментальная и клиническая фармакология. -2015. –Т. 78, № 5. –С. 13-18.
- Makarenko I.E., Faustova N.M., Pozharitskaya O.N., Makarova M.N., Shikov A.N. Evaluation of the grin sea urchin extracts incretins effect// Abstracts. Phitopharm. 2016. Obzory po klinicheskoj farmacologii i lekarstvennoj terapii. – 2016. – Vol. 14. – P. 43. EVALUATION OF THE GRIN SEA URCHIN EXTRACTS INCRETINS EFFECT
- Goryachev M.A., Makarova M.N. Features of the glucose tolerance test in small laboratory rodents (mice and rats) // International Bulletin of Veterinary Medicine. – 2016, № 3. C. 155-159. SUMMARY. Glucose tolerance test (GTT) is a laboratory procedure for estimation of glucose metabolism in the body, when first fasting glucose level is measured, and then – it is checked every 30 minutes within 2 hours after glucose load has been given. In a “classical test” glucose concentration is measured five times: before glucose load (fasting – baseline), in 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes afterwards. In clinical practice, depending on the purposes, the analysis can be performed two or three times. A standard glucose load for a man is 75 g of glucose irrespectively of body weight. The chart characterizing different stages of glucose metabolism is built on the results of the test. Increase of glucose level after a glucose load is called hyperglycemic phase and it reflects characteristics of glucose absorption. Decrease of glucose level is called hypoglycemic phase and it indirectly reflects the rate of insulin secretion and sensitivity of tissues to this hormone. The last phase is disturbed in patients with pre-diabetes (impaired glucose tolerance) or diabetes mellitus type 2. Evaluation of hypoglycemic phase has a leading role in the diagnostics of diabetes in patients, if the disease has asymptomatic character. Furthermore, using GTT one can calculate two additional criteria, hyperglycemic and post-glycemic indexes, which are also used for estimation of glucose metabolism. Due to the fact that GTT is highly informative and easy to perform it is widely used in pre-clinical trials. Procedure for performing GTT described in this article makes it possible to obtain reliable results and adequately estimate condition of carbohydrate metabolism in laboratory animals [Full text is available in Russian].
- Gushchin Y.A., Muzhikyan A.A., Selezneva A.I., Makarova M.N. Complex morphological evaluation of atherosclerotic damage of the aorta of rabbits in the experiment // Atherosclerosis and dyslipidemia. – 2017. – Vol. 1. – P. 50-59.
- Шекунова Е.В., Кашкин В.А., Титов М.И., Елисеев И.И., Мужикян А.А., Макарова М.Н., Макаров В.Г. Изучение нейропротекторных свойств нового эксенатида, содержащего олигоаргининовый вектор, на модели вызванного стрептозотоцином диабета у крыс // Материалы Рос. научной конференции, посвященная 125-летию академика С.В. Аничкова, Фармакология регуляторных нейропептидов, Санкт-Петербург, 9-11 октября 2017 г. –С. 79-80.
- Makarova M., Makarov V. Diet-induced models of metabolic disorders. Report 5: Experimental hypertension // Laboratory Animals for Science. – 2019. – Vol. 1. – P. 1-11. https://doi.org/10.29296/2618723X-2019-01-08 SUMMARY. Despite the use of a huge number of new drugs, hypertension (AG) remains the most common disease and one of the main causes of mortality in the world. However, the lack of a full understanding of the pathogenesis of AG does not allow for an effective cure of this disease: while all drugs remove only the main symptom – high blood pressure (BP). In this regard, the need for further research on the pathogenesis of AG, the search for means of its prevention and treatment is not in doubt. The analysis of modern literature allowed to establish that for the induction of salt AG the most commonly used diets containing 4% to 8% NaCl, rarely administered NaCl with drinking water in the form of 1% solution. The duration of NaCl application varies from 10 days to 36 weeks. BP increases in direct proportion to the amount of salt in the diet of animals and the duration of NaCl. The maximum rise in BP occurs on the 40-50 day stay on a high-salt diet, then there is a decrease in BP. The best models for high-salt suitable for AG spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) who have systolic BP reaches 190 mm Hg and above, also salt-sensitive rats Dahl – 170 mm Hg and above. Some researchers use diets containing 60% fructose, or diets with 10% fructose added to water for drinking. They use mainly rats, an outbred wild lines (Sprague Dawley, etc.). However, for models using fructose require longer periods for the development of AG than for salt – from 8 weeks to 12 months (most often – 3-5 months). Therefore, the most effective are high-salt models of AG (8% NaCl in the diet) with the addition of 4 or 10% fructose to drinking water. To accelerate the development of AG content of potassium, calcium and zinc in the diet should be less than normal, and the amount of phosphorus, on the contrary, above normal. It is also possible to study AG on models of metabolic syndrome, obesity and kidney disease. To assess the development of AG used indicators of BP (systolic, diastolic, average), metabolism, endothelial, kidney, oxidative stress, proinflammatory cytokines, heart mass, urine volume and others [Full text is available in Russian].
- Kovaleva M., Gushchin Ya., Makarova М., Makarov V. A comparative study of the use of highcalorie diets enriched by different number of lipids for modeling metabolic syndrome // Laboratory Animals for Science. – 2019. – Vol. 1. – P. 1-11. https://doi.org/10.29296/2618723X-2019-01-04 SUMMARY. Today, one of the main reasons for the spread of insulin resistance, which subsequently leads to the development of obesity, type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome (MS), is the peculiarity of modern human eating behavior, its propensity to unlimited intake of high-calorie food. Nutrition is an element of a lifestyle that can be controlled and thus directly affect the health of both the individual and the nation as a whole. In this regard, of particular interest is the simulation of MC in laboratory animals using high-calorie diets. The model of alimentary obesity allows to understand the reasons for the development and progression of MS and to investigate potential drugs for its prevention and treatment. The aim of this study was to compare the severity of manifestations of pathological changes in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism against the background of the experimental metabolic syndrome induced by diets enriched with different lipid content: D12451 (45% kcal from fat) and D12492 (60% kcal from fat) in laboratory mice. Since the 4th week of the study, a significant increase in body weight was observed in laboratory mice fed high-calorie diets enriched with lipids, which at the end of the study was about 10% in the D12451 group (45% kcal from fat) and 30% in the D12492 group (60% kcal from fat). A moderate hyperglycemia and a tendency to increase the activity of the enzyme dipeptidylpeptidase type 4 was revealed. At week 21, in the group of animals that received D12492 (60% kcal from fat) during the glucose tolerant test, development of glucose tolerance was established. On the background of application of both high-calorie fat diets in laboratory mice, structural and functional changes in the liver were revealed, which was reflected in a decrease in the glycogen content in the liver and development of large and small-dropped fatty liver disease. Our findings support show that diets enriched with lipids can be used by 45% and 60% to simulate the experimental metabolic syndrome in young 8weeks of age outbred male mice. The optimal timing of the formation of stable pathological changes characteristic of the alimentary metabolic syndrome was established. They were: 13 weeks – against the background of D12451 application – kcal from fat 45% and 17 weeks against the background of application D12492 – kcal from fat 60%. It should be noted that the use of a more highcalorie D12492 diet with a lipid content of 60% leads to metabolic disturbances not only of lipid but also carbohydrate metabolism, which is reflected in the development of glucose tolerance established during the glucose tolerant test [Full text is available in Russian].
- Uspenskiy U.P., Balukova E.V., Makarov V.G., Makarova М.N., Kovaleva M.A. The Study of the Specific Activity of Amitriptyline and Profluzak on a Model of Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Spontly Hypertensive Animals // Translational Medicine. – 2019. – Vol. 6(1). – P. 58–68. https://doi.org/10.18705/2311-4495-2019-6-1-58-68 SUMMARY. Background.The direct pathophysiological effects of depression on the components of MS lead to the development of atherosclerosis risk factors. The use of antidepressants minimizes life-threatening clinical manifestations of coronary artery disease and the formation of a pathological stereotype of eating behavior. Objective. To study the specific activity of antidepressants on induced metabolic syndrome in spontaneously hypertensive animals. Design and methods. Work performed on rats (males line SHR). The intact group was on a standard diet, the control group and the groups that received the drugs (amitriptyline and intraludial vaccine, 16.2 mg/kg and 1.7 mg/kg respectively, once a day for five weeks) — on the “cafeteria diet”. Results. With the induction of MS in the groups receiving the diet “cafeteria diet” there was an increase in body weight by 5 % relative to intact animals, fasting glucose levels exceeding 7.2 ± 0.9 mmol/l, a tendency to an increase in serum cholesterol (CS) blood more than 2.0 ± 0.1 mmol/l. Against the background of the use of the studied drugs, there was a statistically significant reduction in feed intake by 77 and 59 % and a decrease in body weight relative to the control group by 10 and 8 % respectively. Significant dynamics of indicators of GTT, cholesterol, TG, LDL and HDL with the use of antidepressants was not observed. Conclusion. A pronounced anti-bulimic effect of the studied drugs, manifested in a decrease in feed intake, a decrease in body weight, was noted. Positive dynamics on carbohydrate and lipid exchanges, indicators of blood pressure, behavioral activity of animals was not observed [Full text is available in Russian].



